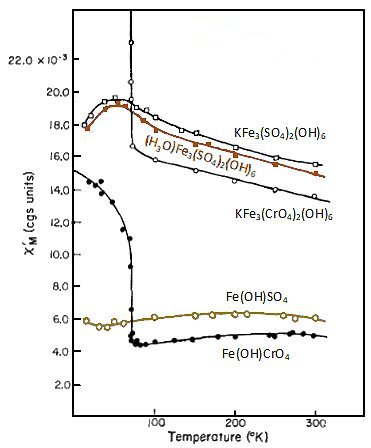
Molar magnetic susceptibility vs temperature for the basic iron suphates and chromates.
The magnetic behavior
and infrared
spectroscopic features of KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6,
(jarosite), (H3O)Fe3(SO4)2(OH)6,
(hydronium jarosite), KFe3(CrO4)2(OH)6,,
Fe(OH)SO4 (basic iron sulfate) and Fe(OH)CrO4,
(basic iron chromate)
are reported. Spectroscopic data are in accord with X-ray data which
show that KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6,
(H3O)Fe3(SO4)2(OH)6,
KFe3(CrO4)2(OH)6,
are isostructural with KAl3(SO4)2(OH)6
(akunite). All the species exhibit negative deviations from Curie-Weiss
behavior over the temperature range 300-76 K. The compounds KFe3(CrO4)2(OH)6
and Fe(OH)CrO4 undergo ferrimagnetic transitions at
73 and 71 K,
respectively. Maxima occur in the susceptibilities of KFe3(SO4)2(OH)66
and (H3O)Fe3(SO4)2(OH)6
at
45 and 50 K.
