 |
|
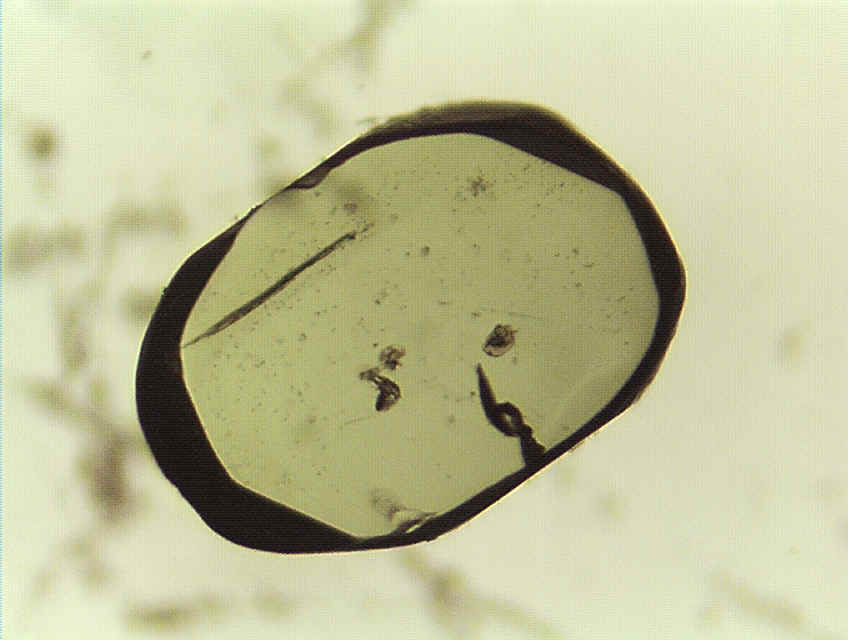
| Diopside in calcite from the Cascade Slide Xenolith, Adirondack Mountains, NY | An oriented slab of diopside about 1.5 mm in length. |
Elizabeth A. Johnson, George R. Rossman
Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125 USA
M. Darby Dyar
Department of Earth and Environment, Mount Holyoke College, South Hadley, MA 01705 USA
and John W. Valley
Department of Geology and Geophysics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706 USA
American Mineralogist 87, 899-908.
Abstract
The concentration of structural OH in diopside was determined for four granulite facies siliceous marble samples from the Adirondack Mountains, New York, using FTIR spectroscopy. Single-crystal polarized IR spectra were measured on (100) and (010) sections of diopside. The relative intensities of four OH bands in the 3700-3200 cm-1 region vary among the samples, with the 3645 cm-1 band dominating the spectra of diopside from a xenolith at Cascade Slide. Total OH content in the diopsides ranges from 55 to 138 ppm H2O by weight. The OH concentration in diopside increases monotonically with increasing fH2O for the sample, as estimated using oxygen isotope systematics for these samples from Edwards and Valley (1998). There is no significant variation in OH content within a single diopside grain or among diopside grains from the same hand sample. Charge-coupled substitution with M3+ and Ti4+ in the crystal structure may have allowed retention of OH in the diopside structure during and after peak metamorphism (~750ºC, 7-8 kbar). The Cascade Slide diopsides have an Fe3+/Fe2+ of 0.98, compared to Fe3+/Fe2+ (0 to 0.05) for the other samples, implying that some loss of hydrogen through oxidation of Fe was possible in this sample. This is the first study we know of which shows that the OH content in anhydrous minerals from natural samples affects the rate of oxygen isotope diffusion.
Figure Captions (PDF format)
Figure 1 (PDF format)
Figure 2 (PDF format)
Figure 3 (PDF format)
Figure 4 (PDF format)
Figure 5 (PDF format)
Figure 6 (PDF format)
Table 1 (PDF format)
Table 2 (PDF format)
Table 3 (PDF format)
 |
|
| Diopside in calcite from the Cascade Slide Xenolith, Adirondack Mountains, NY | An oriented slab of diopside about 1.5 mm in length. |